这道题的思路是先构建二叉树,然后层序遍历二叉树。将问题拆解:1.如何构建二叉树。2.如何测层序遍历二叉树。
1.构建二叉树
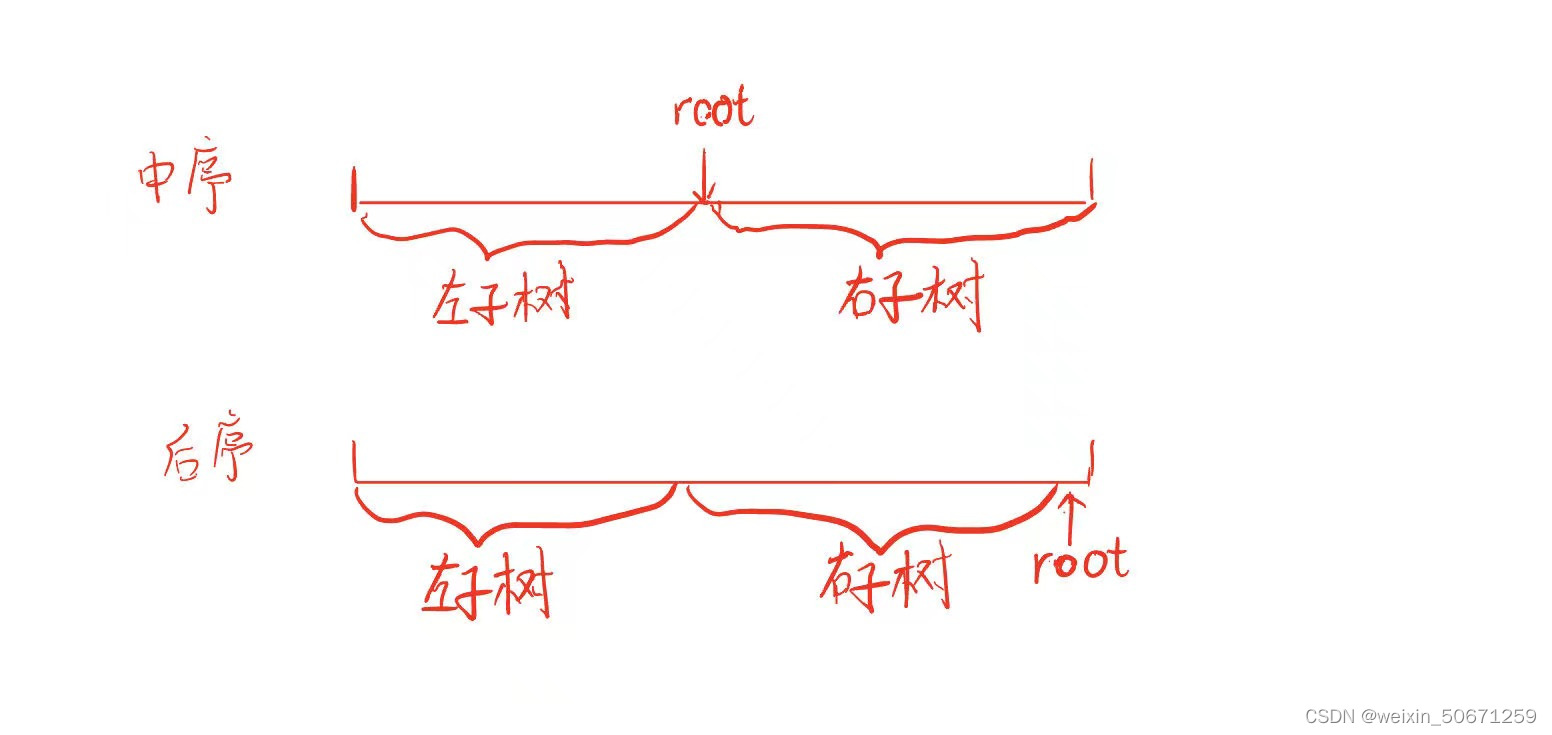
首先我们要知道一棵二叉树可由它的中序遍历和后序遍历确定:
(1)后序遍历的最后是该树或子树的根
(2)中序遍历根的左右分左子树和右子树
通过后序遍历找到根的值,然后再到中序序列里找到根的位置再将该树分为左子树与右子树 。不断递归即可通过中序和后序重塑一棵树。
int build(int il,int ir,int pl,int pr)//il,ir为中序遍历的左右下标;pl,pr为后序遍历的下标 { int root=postorder[pr]; //后序遍历的最后一位是树的根 int k=pos[root];//pos数组记录了每个数的下标 //根将中序遍历分成两部分,分别是左子树、右子树 //l,r 为map,记录左右子树。 if(il<k) l[root]=build(il,k-1,pl,k-1-il+pl);//k-1-il=x-pl //左子树在中序序列中为[il,k-1] ,在后序序列中左子树长度相同,从pl开始,故 x-pl=k-1-il,x即右端点为k-1-il+pl; if(k<ir) r[root]=build(k+1,ir,pr-ir+k,pr-1);// pr-1-x=ir-k-1 //右子树在中序序列中为[k+1,ir] ,在后序序列中右子树长度相同,到pr-1结束,故 pr-1-x=ir-k-1,x即左端点为pr-ir+k; return root; }
2.bfs层序遍历树
void bfs(int root) { queue<int> q; q.push(root); int flag=1;//标记是否第一次输出,第一次输出数组,后续输出空格数字;为了最后数字没有输出空格(pat格式要求) while(q.size()){ int x=q.front(); q.pop(); if(flag){ cout<<x; flag=0; } else cout<<" "<<x; if(l.count(x)) q.push(l[x]);//如果左节点在,则放入队列 if(r.count(x)) q.push(r[x]);//如果有右节点,则放入队列 } }
整体代码:
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<unordered_map> #include<queue> using namespace std; const int N=40; int postorder[N],inorder[N]; unordered_map<int,int> l,r,pos; int build(int il,int ir,int pl,int pr) { int root=postorder[pr]; int k=pos[root]; if(il<k) l[root]=build(il,k-1,pl,k-1-il+pl);//k-1-il=x-pl if(k<ir) r[root]=build(k+1,ir,pr-ir+k,pr-1);// pr-1-x=ir-k-1 return root; } void bfs(int root) { queue<int> q; q.push(root); int flag=1; while(q.size()){ int x=q.front(); q.pop(); if(flag){ cout<<x; flag=0; } else cout<<" "<<x; if(l.count(x)) q.push(l[x]); if(r.count(x)) q.push(r[x]); } } int main() { int n; cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>postorder[i]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ cin>>inorder[i]; pos[inorder[i]]=i;//pos存放每个数的下标 } int root=build(0,n-1,0,n-1);//构建二叉树 bfs(root);//层序遍历 return 0; }